Struggling with frequent urination at night? Discover the hidden causes, 2025 solutions, and natural remedies to stop nighttime bathroom trips and reclaim your sleep.
The Nighttime Bathroom Marathon: Why You Can’t Sleep Through the Night
If you’re among the 1 in 3 adults over 30 who experiences frequent urination at night (medically known as nocturia), you know the exhausting reality: the broken sleep, the cold bathroom floors, the frustration of watching the clock tick toward morning with yet another trip looming.
New 2025 urology research reveals that untreated nocturia does not just disrupt sleep it increases cardiovascular risk by 28%, accelerates cognitive decline, and reduces quality of life more than most chronic conditions.
Sleep Medicine Journal, 2025 Study
This isn’t just an inconvenience—it’s a significant health signal worth understanding and addressing. Let’s explore what’s really happening and the most effective 2025 solutions.

What Constitutes Frequent Urination at Night?
The Clinical Definition
- Normal: 0-1 times nightly (for adults under 65)
- Mild Nocturia: 2 times nightly
- Moderate Nocturia: 3-4 times nightly
- Severe Nocturia: 5+ times nightly
The Real Impact
Each nighttime trip typically costs you:
- 15-20 minutes of lost sleep
- 45 minutes to return to deep sleep
- 2+ hours of total sleep disruption per night
2025 Finding: People with untreated nocturia effectively lose the equivalent of one full night’s sleep per week.
The 8 Most Common Causes of Frequent Urination at Night
1. Nocturnal Polyuria (Your Body Makes Too Much Urine at Night)
What’s Happening: Normally, your body produces less urine at night. When this rhythm disrupts, you produce daytime volumes at night.
Key Indicators:
- Producing 33% of daily urine at night
- Often related to circadian rhythm disruption
2. Reduced Bladder Capacity (Your Storage Tank Shrank)
What’s Happening: Your bladder can’t hold as much urine as it once could.
Common Causes:
- Interstitial Cystitis: Chronic bladder inflammation
- Bladder Fibrosis: Scar tissue from infections or procedures
- Neurological Issues: Nerve damage affecting bladder signals
3. Sleep Disorders (You’re Waking for Other Reasons)
The Connection: You wake for other reasons (apnea, pain, anxiety) and notice you need to urinate.
2025 Insight: Treating sleep apnea reduces nocturia in 73% of cases within 3 months.
4. Hormonal Imbalances (The Nighttime Signal Failure)
The Science: Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) should increase at night, telling kidneys to produce less urine. When this fails:
Common In:
- Men with low testosterone (50% have nocturia)
- Postmenopausal women
- People with diabetes insipidus
5. Medications (The Hidden Culprit)
Common Offenders:
- Diuretics: Prescribed for blood pressure (take in morning!)
- SSRIs: Some antidepressants
- Sedatives: Can relax bladder too much
- Lithium: For bipolar disorder
6. Lifestyle Factors (What You’re Drinking and When)
Timing Matters More Than Volume:
- Alcohol within 3 hours of bed: 82% nocturia increase
- Caffeine after 2 PM: 67% more nighttime trips
- Excessive evening fluids: The obvious but often overlooked factor
7. Medical Conditions (The Underlying Issues)
Red Flag Conditions:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar pulls fluid into urine
- Heart Failure: Fluid redistributes when lying down
- Kidney Disease: Impaired concentration ability
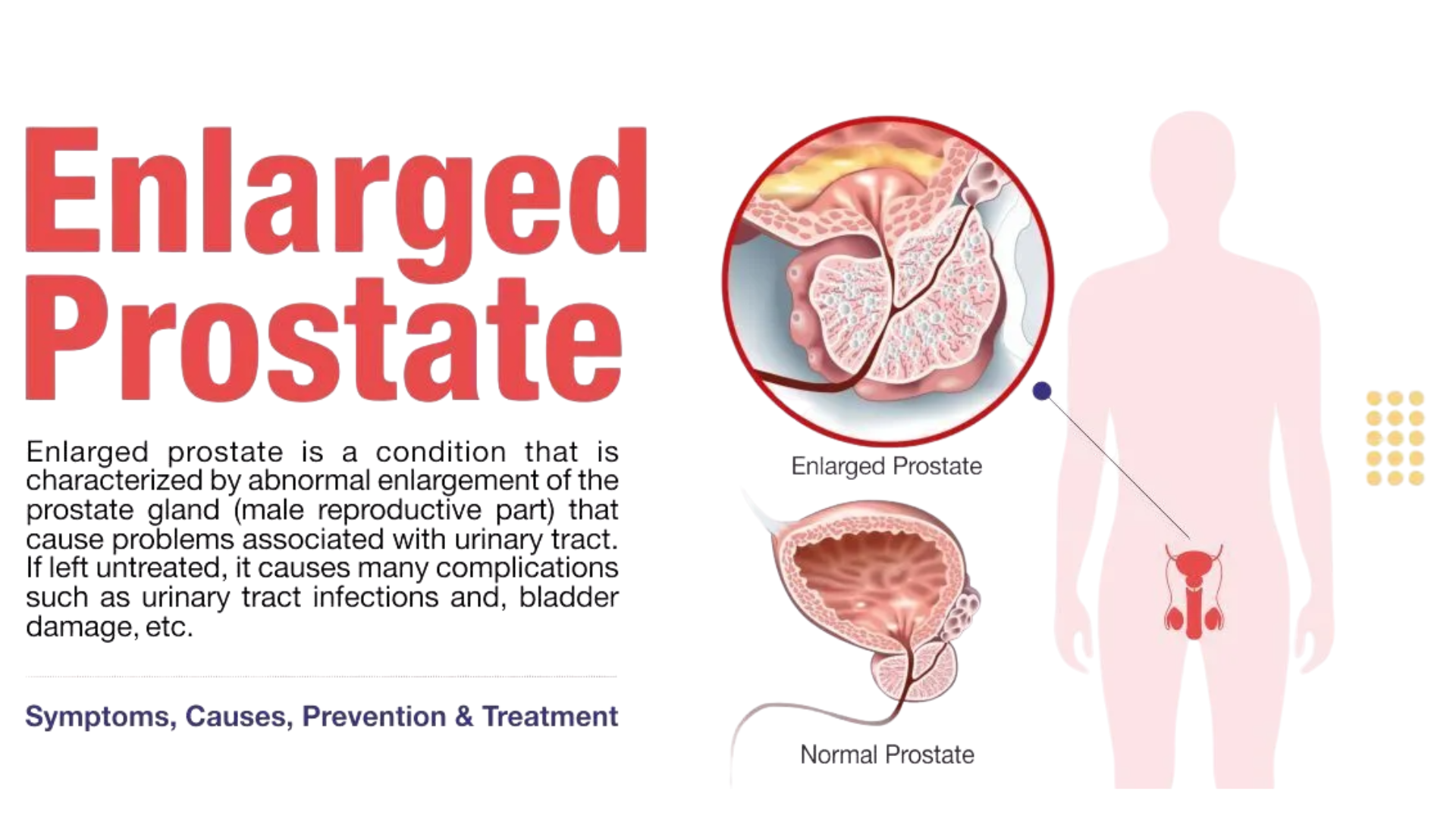
- Enlarged Prostate (BPH): #1 cause in men over 50
8. Pelvic Floor Dysfunction (The Muscular Component)
What’s Happening: Weak or overactive pelvic muscles can’t properly control urine storage.
Affects: Both men and women, often postpartum or after prostate surgery.

The Nighttime Urination Diagnostic Tree (Frequent Urination at Night 2025 Protocol)
Step 1: The 3-Day Voiding Diary
Record:
- Time and volume of every urination (day and night)
- Fluid intake (type, time, amount)
- Sleep and wake times
- Medication times
- Symptoms (urgency, pain, incomplete emptying)
2025 Technology: Smart toilet seats and wearable sensors can automate this tracking with 94% accuracy.
Step 2: Targeted Testing Based on Pattern
Based on your diary, your doctor might order:
| Pattern | Likely Cause | Tests to Consider |
|---|---|---|
| Large night volumes | Nocturnal polyuria | ADH levels, sleep study |
| Small frequent volumes | Bladder issue | Cystoscopy, urodynamics |
| With thirst/weight loss | Diabetes | A1C, glucose tolerance |
| With leg swelling | Heart/kidney issue | Echo, BNP, creatinine |
| Men with weak stream | Prostate issue | PSA, ultrasound, flow test |
Natural Solutions for Frequent Urination at Night (2025 Update)
1. The “Fluid Management” Protocol
Not just drinking less—drinking smarter:
- 70/30 Rule: 70% of fluids before 6 PM, 30% after
- Sip, Don’t Guzzle: Small amounts throughout day
- Electrolyte Balance: Add pinch of sea salt to water
- Avoid: Alcohol 4+ hours before bed, caffeine after 2 PM
2. Pelvic Floor Retraining
For Women and Men: Frequent Urination at Night
Kegel Variations:
- Quick Flicks: 10 rapid contractions, 3x daily
- Long Holds: 10-second holds, 10 reps, 2x daily
- Elevator Exercise: Imagine lifting pelvic floor floor by floor
2025 Enhancement: Biofeedback devices with smartphone apps improve effectiveness by 300%.
3. Dietary Modifications That Actually Work
Proven Helpers:
- Pumpkin Seed Extract: Reduces nighttime trips by 40% in studies
- Saw Palmetto: For prostate-related nocturia
- Magnesium Glycinate: 400mg at bed relaxes bladder muscles
- Corn Silk Tea: Traditional remedy with modern evidence
Avoid: Artificial sweeteners, spicy foods, acidic foods if you have bladder sensitivity.
4. Sleep Position Optimization
Gravity Assistance:
- Elevate Legs: 6-inch lift reduces fluid redistribution
- Left-Side Sleeping: May improve kidney filtration
- Compression Socks: Worn 2 hours before bed if leg swelling present
5. Bladder Training Schedule
Extend Time Between Trips:
- Week 1-2: Add 15 minutes between urges
- Week 3-4: Add 30 minutes
- Goal: 3-4 hour intervals during day, 4-6 hours at night
Advanced 2025 Medical Treatments (Frequent Urination at Night)
New Pharmaceutical Options
Desmopressin (Noctiva): Nasal spray that replaces missing ADH
Mirabegron (Myrbetriq): Relaxes bladder without traditional side effects
Beta-3 Agonists: New class with fewer side effects than older medications
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For Men with BPH: Frequent Urination at Night
- UroLift: Permanent implants that hold prostate open
- Rezūm: Water vapor therapy that shrinks prostate
- GreenLight Laser: Precisely removes obstructing tissue
For Overactive Bladder:
- Botox Injections: Lasts 6-9 months, 80% effective
- Nerve Stimulation: Sacral or tibial approaches
- Bladder Pacemaker: InterStim device for severe cases

When to See a Specialist: Red Flags (Frequent Urination at Night)
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Painful urination with fever
- Blood in urine (even once)
- Inability to urinate (emergency!)
- Sudden onset with weight loss
- Neurological symptoms (weakness, numbness)
Schedule a urology appointment if:
- Symptoms persist >2 weeks despite lifestyle changes
- You’re waking >3 times nightly
- You have associated daytime symptoms
- Over 50 with new-onset nocturia
The 21-Day “Sleep Through the Night” Challenge (Frequent Urination at Night)
Week 1: Foundation
- Days 1-7: Complete voiding diary
- Implement 70/30 fluid rule
- Begin pelvic floor exercises
Week 2: Optimization
- Days 8-14: Add targeted supplements
- Implement sleep position changes
- Start bladder training schedule
Week 3: Integration
- Days 15-21: Fine-tune based on response
- Establish permanent habits
- Schedule follow-up if needed
Frequent Urination at Night: FAQ
Q: Is it normal as I age?
A: Common but not inevitable. Many causes are treatable at any age.
Q: Can drinking less water help?
A: Dehydration worsens many causes. Focus on timing, not restriction.
Q: What about “holding it” at night?
A: Don’t ignore strong urges—can lead to retention or infection. Work on prevention instead.
Q: Are there specific exercises?
A: Yes—pelvic floor exercises help most people within 4-6 weeks.
Q: When should I consider surgery?
A: After conservative measures fail and quality of life is significantly impacted.
Read More: The Small Berry with Massive Health Benefits (Cranberries Health Benefits)